Mobile Apps Pentesting
... > Vulnerability Assessment / Penetration Testing (VAPT) > Mobile Apps Pentesting
Mobile Apps Pentesting
Mobile applications have become an integral part of our daily lives. The apps handle and store sensitive data, making them attractive targets for attackers. This makes app developers vulnerable for reputation damage, legal issues and financial losses. Let Secura help you identify security weaknesses in your apps.

Your Challenges
- How to prevent hackers from gaining unauthorized access to sensitive data in the app.
- How to prevent hackers from controlling the device remotely.
- How to ensure the app is secure in accordance with recognised industry standards.
How We Support You
Secura helps large and medium sized organizations all over Europe raise their cyber resilience. We know the importance of secure mobile apps, for the reputation of your company and the safety of your customers. We can test your mobile application against recognised standards.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR YOUR PENTEST
Secura Mobile App Testing
Every mobile application is different. So we start by identifying context-specific threats. That will allow us to maximally tailor the assessment to the application in question.
Next we study and test the mobile application thoroughly for design flaws, configuration errors and programming errors. We combine the personal experience of our testers with knowledge available in the global application security community.
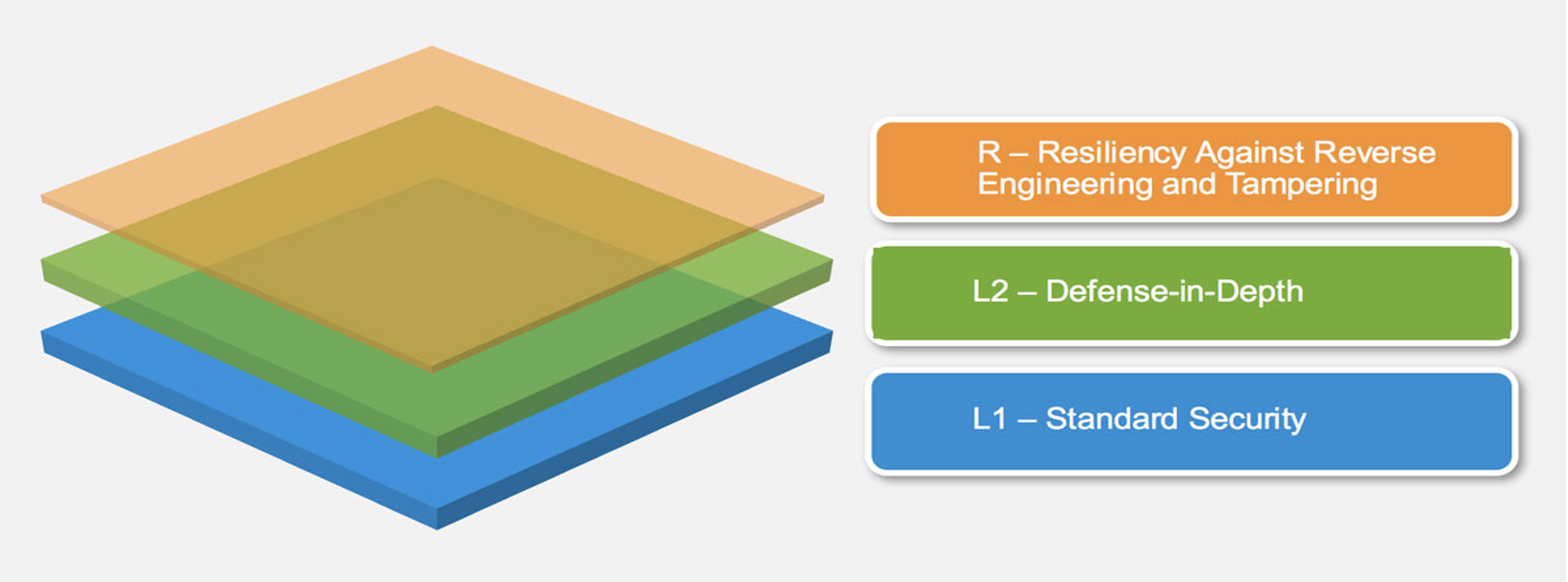
3 Layers of the Mobile Application Security Verification Standard
OWASP Mobile Application Security Verification Standard
As a baseline to define our application-tailored assessments, Secura follows the OWASP Mobile Application Security Verification Standard (MASVS).
This standard defines three levels of security requirements and testing rigor. Each level is designed to build on the previous level, providing a progressive approach to mobile security. Secura follows the levels of MASVS as a starting point to define the thoroughness of an application test.
MASVS-L1
MASVS-L1 is the baseline and includes a set of requirements that every mobile application should meet in order to provide a basic level of security.
MASVS-L2
MASVS-L2 includes more advanced security controls and more defense-in-depth security mechanisms for the mobile application.
MASVS-R
MASVS-R focuses specifically on the resilience of mobile applications to attacks in which the Operating System and User are not trusted. It includes a set of verification requirements designed to ensure that mobile applications are designed and built to be resilient to, for example tampering and reverse engineering.
Fully Tailored to Your Needs
For the majority of applications, our default coverage based on MASVS-L1 is sufficient to ensure that the application is protected against the most prevalent threats. Depending on the application’s complexity and needs, MASVS-L2 and MASVS-R can be covered as well.
Testing levels for different types of mobile applications
MASVS-L1 |
Offered by default for all mobile applications. |
MASVS-L1 + MASVS-R |
For mobile applications where intellectual property is a business goal. |
MASVS-L2 |
For mobile applications that handle confidential business data or financial transactions. |
MASVS-L2 + MASVS-R |
For mobile applications that handle highly sensitive data, for example health records. |
Regulations and industry standards may require organizations to implement specific security controls and testing procedures for mobile applications. For example, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) requires that organizations that accept credit card payments through mobile applications comply with a set of specific requirements for secure development and test.
0%
Mobile apps with high-risk security flaw
0
NPS Score Secura Mobile App Pentests
I'd like to know more about Mobile Apps Pentesting

Related Services
Web Applications / API's Pentesting
Wi-Fi Pentesting
Hardware / IoT Pentesting
Infrastructure Pentesting
Why choose Secura | Bureau Veritas
At Secura/Bureau Veritas, we are dedicated to being your trusted partner in cybersecurity. We go beyond quick fixes and isolated services. Our integrated approach makes sure that every aspect of your company or organization is cyber resilient, from your technology to your processes and your people.
Secura is the cybersecurity division of Bureau Veritas, specialized in testing, inspection and certification. Bureau Veritas was founded in 1828, has over 80.000 employees and is active in 140 countries.








